Crypto Buy Bitcoin Eth Your Guide To Digital Assets
crypto buy bitcoin eth sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
In today's rapidly evolving financial landscape, cryptocurrencies have emerged as a revolutionary force, reshaping how we perceive value and conduct transactions. This guide dives deep into the world of Bitcoin and Ethereum, exploring their origins, functionalities, and the step-by-step process of acquiring these digital assets. Whether you're a curious newcomer or looking to refine your investment strategy, understanding the nuances of these cryptocurrencies is essential.
Overview of Cryptocurrency

Cryptocurrency has become a significant topic in the financial world, reshaping how we think about currency. It is a digital or virtual form of money that utilizes cryptography for security, making it difficult to counterfeit or double-spend. The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies, operating on blockchain technology, sets them apart from traditional currencies. The origins of cryptocurrency can be traced back to the introduction of Bitcoin in 2009, created by an anonymous entity known as Satoshi Nakamoto.
Since then, the evolution of cryptocurrencies has been rapid, with thousands of alternative coins emerging, each with unique features and purposes. Cryptocurrencies are characterized by their decentralized control, transparency in transactions, and limited supply, which contrast with the centralized nature of traditional fiat currencies controlled by governments and central banks.
Understanding Bitcoin

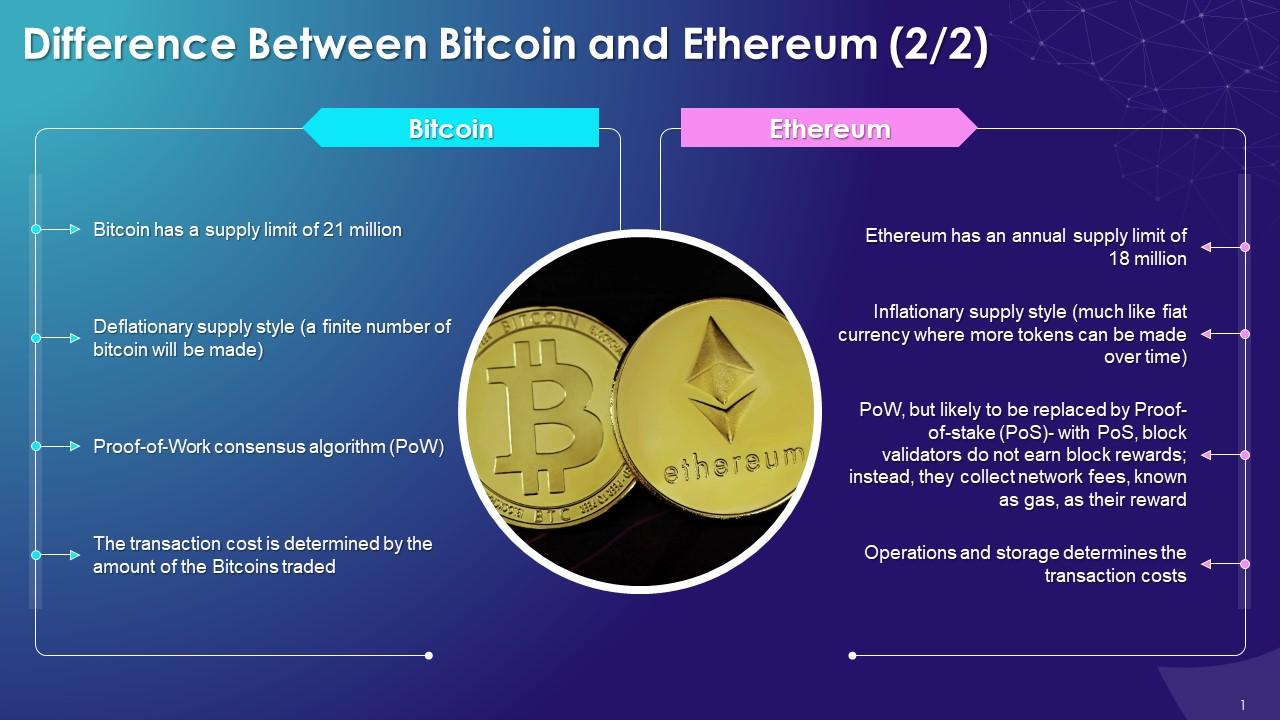
Bitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, created in 2009. It operates on a decentralized network of computers that validate and record transactions on a public ledger known as the blockchain. One of the significant advantages of investing in Bitcoin is its potential for high returns, as it has seen substantial price appreciation over the years. However, it also comes with disadvantages, such as price volatility and regulatory uncertainties.When comparing Bitcoin to other cryptocurrencies, it holds the largest market share and is often considered the gold standard of the crypto market.
Despite its dominance, many alternative cryptocurrencies (altcoins) offer unique features and use cases, contributing to their growing popularity alongside Bitcoin.
Exploring Ethereum (ETH)
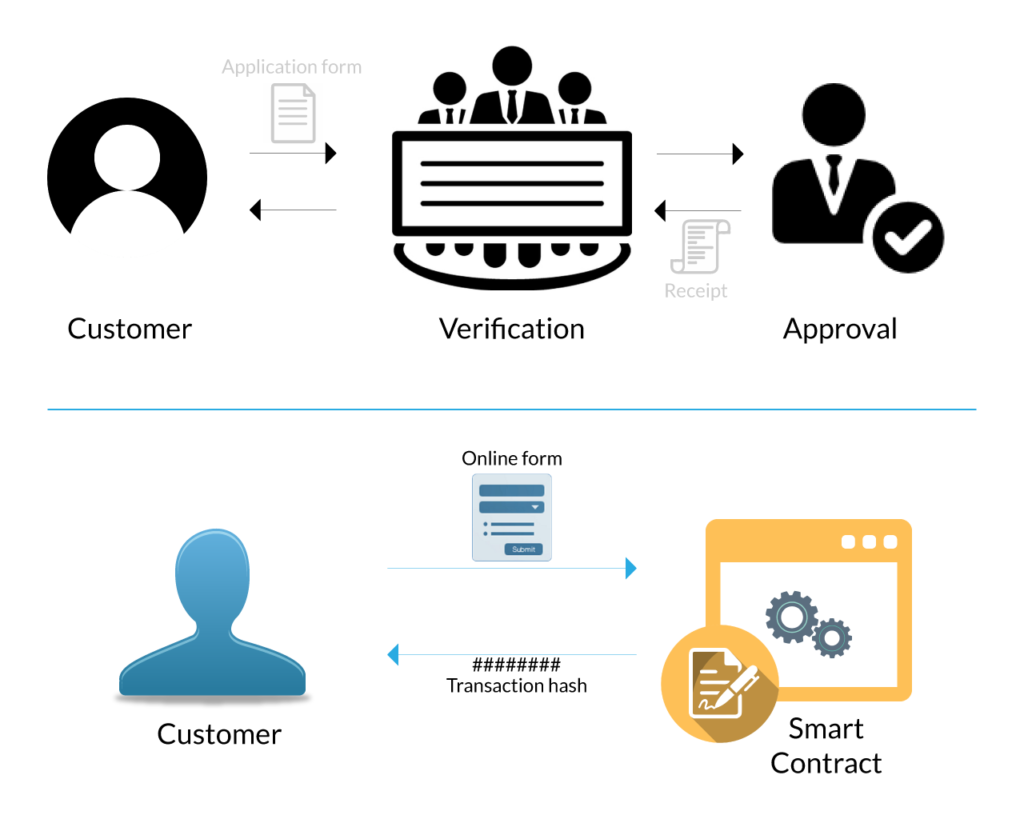
Ethereum distinguishes itself from Bitcoin primarily through its ability to support smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This allows developers to build decentralized applications (dApps) on the Ethereum platform, opening up a myriad of possibilities beyond just currency transactions.Smart contracts function by automatically executing and enforcing agreements once predetermined conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries.
The potential use cases for Ethereum extend to various sectors, including finance, supply chain management, and even digital art through non-fungible tokens (NFTs), showcasing its versatility in the blockchain space.
Steps to Buy Bitcoin and Ethereum

Purchasing Bitcoin or Ethereum can be a straightforward process if you follow the right steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
- Choose a cryptocurrency exchange: Research and select a reliable platform that offers Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Create an account: Sign up on the chosen exchange by providing necessary information and completing any required verification processes.
- Deposit funds: Link your bank account or use another payment method to deposit funds into your exchange account.
- Place an order: Navigate to the market section of the exchange and place a buy order for Bitcoin or Ethereum.
- Storage: Transfer your purchased coins to a secure wallet to keep your investment safe.
For buying Ethereum, the steps are similar, but it’s important to check if the exchange supports ETH purchases and any specific fees associated with the transaction.
Methods of Storing Cryptocurrencies
Storing cryptocurrencies securely is crucial for protecting your investment. There are various types of wallets available:
- Hot Wallets: These wallets are connected to the internet, making them convenient for frequent transactions but more vulnerable to hacks.
- Cold Wallets: These are offline wallets that offer enhanced security, ideal for long-term storage of cryptocurrencies.
- Hardware Wallets: Physical devices that store your private keys offline, providing an extra layer of security against online threats.
It’s advisable to implement security measures such as two-factor authentication and strong passwords when storing cryptocurrencies to safeguard against unauthorized access.
Trading Strategies for Cryptocurrencies
Investing in Bitcoin and Ethereum requires a well-thought-out trading strategy. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Day Trading: Involves buying and selling on short-term movements, requiring active monitoring of the market.
- HODLing: A long-term strategy where investors hold onto their cryptocurrencies despite market fluctuations, based on the belief in their future value.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: This strategy involves regularly purchasing a fixed dollar amount of cryptocurrency, regardless of price, which can reduce the impact of volatility.
Market analysis and trend recognition are essential in crypto trading, as they help investors make informed decisions based on price movements and market sentiment.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory environment surrounding cryptocurrencies varies significantly across the globe. Countries like the United States and Canada have established frameworks to regulate cryptocurrency exchanges, while others, like China, have imposed strict bans on cryptocurrency transactions and mining.Regulations impact the buying and trading of Bitcoin and Ethereum by introducing compliance requirements for exchanges, tax obligations, and consumer protections. Understanding the regulatory landscape is crucial for investors to navigate potential risks and opportunities in different jurisdictions.
Future Trends in Cryptocurrency
Emerging trends in the cryptocurrency market indicate a shift towards greater institutional involvement, with major financial institutions beginning to adopt cryptocurrencies in their portfolios. This trend could significantly impact the legitimacy and acceptance of Bitcoin and Ethereum as viable investment options.Technological advancements, such as the development of Layer 2 solutions for Ethereum, aim to enhance scalability and transaction speeds, addressing some of the current limitations of blockchain technology.
These advancements will likely influence how cryptocurrencies are used in everyday transactions and further integrate them into the global financial system.
Last Point
In conclusion, navigating the waters of cryptocurrency investing can be both exciting and daunting. By arming yourself with knowledge about Bitcoin and Ethereum, their unique features, and practical buying steps, you're better prepared to make informed decisions in this innovative market. As trends continue to evolve, staying updated will empower you to seize opportunities and mitigate risks effectively.
FAQ
What is the best platform to buy Bitcoin and Ethereum?
There are several reputable platforms like Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken that are popular for buying Bitcoin and Ethereum. It's important to choose one based on fees, security, and user experience.
Can I buy a fraction of a Bitcoin or Ethereum?
Yes, you can purchase fractions of Bitcoin and Ethereum, which makes it accessible for investors with varying budgets.
Is it safe to store cryptocurrencies on exchanges?
While exchanges offer convenience, they can be vulnerable to hacks. For enhanced security, it's recommended to use a personal wallet.
What are gas fees on the Ethereum network?
Gas fees are transaction fees required to process transactions on the Ethereum network, varying based on network demand.
How can I track the value of my cryptocurrencies?
There are various apps and websites, such as CoinMarketCap and Blockfolio, that allow you to track the real-time value of your cryptocurrency holdings.